1 - Geographical Location of Cape Verde
Cape Verde is a small island state located in the North Atlantic, approximately 455 km (282 miles) off the west coast of Africa.
It is located between the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer, more precisely between parallels 14º 23′ and 17º 12′ North latitude and meridians 22º 40′ and 25º 22′ West of Greenwich.
The archipelago of Cape Verde is made up of 10 islands (one of which is uninhabited) and 16 islets (5 major and 9 minor). The country's total geographical land area is approximately 4033 km2.
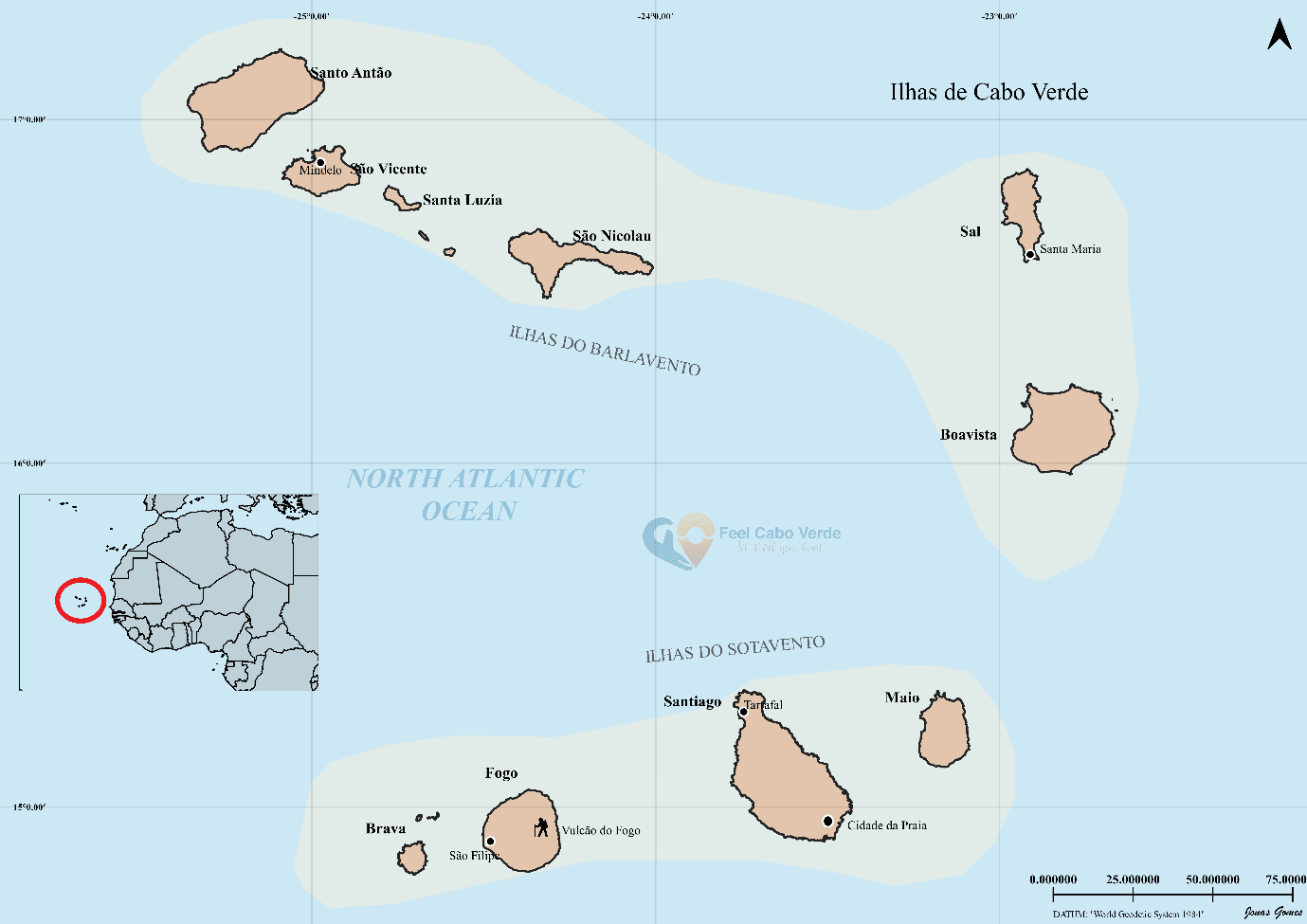
2 - Cape Verde's territorial structure
Cape Verde is made up of ten islands (Santo Antão, São Vicente, Santa Luzia, São Nicolau, Sal, Boa Vista, Maio, Santiago, Fogo and Brava) and several islets.
The islands are grouped into two groups: the Barlavento islands to the north and the Sotavento islands to the south.
Cape Verde is also divided into 22 municipalities, each with its own administration and responsible for different areas such as education, health and infrastructure.
Praia is the country's capital and is located on the island of Santiago, the largest and most populous in the archipelago.
Cape Verde Islands
The islands of Cape Verde are divided into two groups according to the direction of the wind: the Windward Islands (where the wind blows from) and the Leeward Islands (the side opposite the wind, or where it is directed).
The Barlavento islands are located further north and include Santo Antão, São Vicente, São Nicolau, Santa Luzia, Sal and Boavista. The Sotavento islands are located to the south and include the islands of Maio, Santiago, Fogo and Brava.
Ilhéus of Cape Verde
Cape Verde also has 16 complementary islets, the main ones being Branco, Raso, Luís Carneiro, Grande and Ilhéu de Cima. All the islets are uninhabited.
The following table shows the geographical distribution of Cape Verde's main islets.
| Geographical group | Name | Geographical area (km)2) | Location |
| Windward | Bird Islet | – | Between São Vicente and Santo Antão |
| White Islet | 3 | Between Santa Luzia and São Nicolau | |
| Raso Islet | 7 | ||
| Rabo de Junco Islet | – | Coastal area of Sal | |
| Sal Rei Islet | – | Boavista coastal area | |
| Curral Velho Islet | – | ||
| Baluarte Islet | – | ||
| Leeward | Santa Maria Islet | – | Coastal area of the city of Praia, Santiago |
| Sand Islet | – | Brava coastal area | |
| Ilhéu Grande | 2 | ||
| Rombo Islet | – | ||
| Ilhéu de Baixo | – | ||
| Ilhéu de Cima | 1.15 | ||
| King's Islet | – | ||
| Luís Carneiro Islet | 0.22 | ||
| Sapado Islet | – |
Administrative Division of Cape Verde
In terms of administrative division, each island is divided into concelhos or municipalities. Cape Verde has a total of ten islands, 22 municipalities, 24 towns and 32 parishes.
The table below illustrates the division of Cape Verde according to islands, municipalities and cities according to the 2010 update (B.O no. 32 - I Series [Law no. 77/VII/2010]) and the population according to the general housing and population censusof 2021.
Group | Island | Geographical area (km)2) | Population (Census 2021) | Counties | Cities | Parishes by municipality |
Windward | Santo Antão | 785 | 36 950 | Paul | The Doves | Saint Anthony of the Doves |
Porto Novo | Porto Novo | - Saint John the Baptist - Saint André | ||||
Ribeira Grande | Ponta do Sol | - Our Lady of Livramento - Our Lady of the Rosary - Holy Crucifix - St. Peter the Apostle | ||||
Povoação | ||||||
São Vicente | 227 | 75 845 | São Vicente | Mindelo | Our Lady of Light | |
Santa Luzia | 35 | 0 | – | – | – | |
São Nicolau | 343 | 12 306 | Ribeira Brava | Ribeira Brava | - Our Lady of Lapa - Our Lady of the Rosary | |
Tarrafal de S. Nicolau | Tarrafal de S. Nicolau | San Francisco | ||||
Sal | 220 | 33 615 | Sal | Asparagus | Our Lady of Sorrows | |
Santa Maria | ||||||
Boa Vista | 631 | 12 798 | Boavista | King Salt | - Santa Isabel - Saint John the Baptist | |
Leeward | Maio | 275 | 6 330 | Maio | English Port | Our Lady of Light |
Santiago | 991 | 273 988 | Tarrafal | Tarrafal | Santo Amaro Abbot | |
Santa Catarina | Assomada | Santa Catarina | ||||
Santa Cruz | Whiting Rock | Santiago Maior | ||||
Beach | Beach | Our Lady of Grace | ||||
São Domingos | Várzea da Igreja | - Our Lady of Light - Saint Nicholas Tolentine | ||||
São Miguel | Calheta de São Miguel | Saint Michael the Archangel | ||||
Saint Savior of the World | Achada Church | Saint Savior of the World | ||||
São Lourenço dos Órgãos | João Teves | São Lourenço dos Órgãos | ||||
Ribeira Grande de Santiago | Old Town | - Most Holy Name of Jesus - Saint John the Baptist | ||||
Fogo | 476 | 33 754 | Monasteries | Monasteries | Our Lady of Help | |
Saint Philip | Saint Philip | - São Lourenço - Our Lady of the Conception | ||||
Santa Catarina do Fogo | Santa Catarina do Fogo | Santa Catarina do Fogo | ||||
Brava | 63 | 5 647 | Brava | New Sintra | - Saint John the Baptist - Our Lady of the Mount | |
Total | 10 islands | 4033 km2 | 491,233 inhabitants | 22 municipalities | 24 cities | 32 parishes |
Geology and Geomorphology of the Cape Verde Islands
The Cape Verde Islands are volcanic in origin, having been formed by the accumulation of rocks resulting from eruptions on submarine platforms. These rocks rose from a depth of approximately 3000 meters from the seabed, from a large topographic elevation called the Cape Verde Ridge.
Volcanic activity in the archipelago is the result of a hotspotThis is a region of the earth's mantle where columns of hot magma rise through the earth's crust and erupt at the bottom of the sea.
Cape Verde's geological resources
Cape Verde's geological resources mainly include basic rocks with a predominance of basaltic rocks, phonotrachytic rocks and pyroclastic products (bombs, lapilli, sands and tuffs).
Sedimentary rocks are found throughout the archipelago (sand, alluvium, beach gravels, flood deposits and slope deposits), with a greater incidence on the island of Maio, where clays, marls, Jurassic and Cretaceous limestones appear. It should be noted that the percentage of sedimentary rocks is higher than that of magmatic rocks on the island of Maio, unlike the others.
Cape Verde's soils are generally shallow, poor in organic matter, poorly differentiated and rocky. Their substrate is volcanic rock (80% basalt) and sedimentary rock.
Only 10% of the territory's land is potentially arable/cultivable (around 40,000 ha). This is one of the country's main vulnerabilities, since most of what is consumed is imported.
Topography and relief of the Cape Verde islands
Despite their common volcanic origin, the islands of Cape Verde vary in terms of relief and topography. In topographical terms, the islands can be divided into two groups:
- Flat islands: made up of a group of islands of gentle relief, with only a few scattered low peaks; this group includes the islands of Maio, Boa Vista, Sal and Santa Luzia.
- Mountainous islands: characterized by steep and rugged terrain, often with impressive cliffs, gorges and steep slopes.
This group includes the islands of Santo Antão, São Nicolau, Santiago, Fogo and Brava.
The island of São Vicente occupies an intermediate position between these two groups, both in terms of topography and relief.
With the exception of the flatter islands (Santa Luzia, Sal, Boavista and Maio), the relief of the archipelago is considerably rugged. The landscapes vary greatly between the islands, from mile-long beaches (such as Santa Mónica beach on the island of Boavista) to extensive salt pans (on the islands of Sal and Maio), stunning cliffs (mainly on Santo Antão, São Nicolau and Brava) and even an active volcano on the island of Fogo.
Cape Verde's highest points
The following table summarizes the highest points in Cape Verde, their location and respective altitudes.
|
Highlights of Cape Verde |
Island |
Altitude above sea level (meters) |
|
Pico do Fogo |
Fogo |
2829 |
|
Crown top |
Santo Antão |
1979 |
|
Pico da Cruz |
Santo Antão |
1585 |
|
Pico d'Antónia |
Santiago |
1394 |
|
Monte Gordo |
São Nicolau |
1312 |
|
Serra Malagueta |
Santiago |
1064 |
|
Monte Fontainhas |
Brava |
976 |
|
Monte Verde |
São Vicente |
750 |
|
Monte Penoso |
Maio |
431 |
|
Topona |
Santa Luzia |
397 |
|
Mount Estancia |
Boavista |
387 |
|
Monte Grande |
Sal |
252 |
O Cape Verde's highest point is Pico do Fogowith an altitude of 2829 meters above sea level.
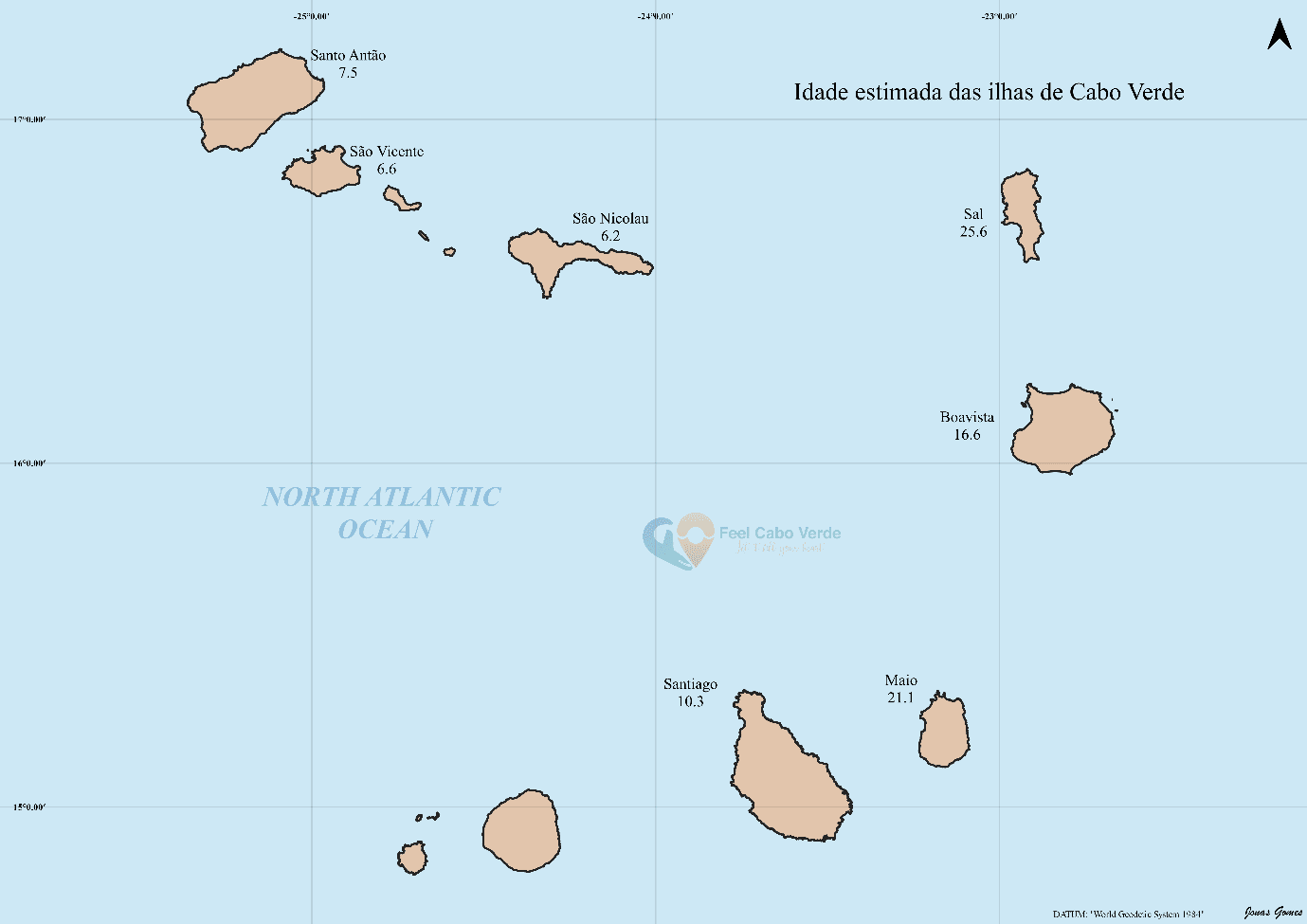
Age of the Cape Verde Islands
Although there is little consensus on the age of the islands, it is estimated that the islands of Sal, Maio and Boavista are the oldest. As a result of strong wind erosion over time, these islands are very sandy and flat.
On the other hand, the islands with a more "wrinkled" and rocky appearance are more recent, with the islands of Fogo and Brava estimated to be the youngest in the archipelago.
The following figure illustrates the approximate age of the Cape Verde islands.
Volcanic activity in Cape Verde
Despite the volcanic origin and some latent volcanic activity throughout the archipelago, it is mostly unnoticeable. The last volcanic eruption in the country occurred in 2014, with no human losses.
Generally, between the premonitory signs of volcanic activity and the explosion of magma to the surface, weeks to months can pass, allowing protective actions to be taken.
Cape Verde's National Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics has 18 seismometric stations distributed throughout the archipelago, which monitor any volcanic activity on the islands. The island of Fogo also has three inclinometer stations that make it possible to monitor the deformation of the ground produced by magmatic intrusions, as a complementary way of monitoring the Fogo volcano. These measures aim to ensure that safety measures are taken in good time in the event of significant volcanic activity.
Conclusion
Cape Verde has a remarkable geological diversity, with impressive landscapes ranging from steep mountains to white sandy beaches and crystal clear waters. This diversity offers great adventure options throughout the islands.
If you are interested in learning more about the topic or would like help exploring the best that Cape Verde has to offer, please contact us.
